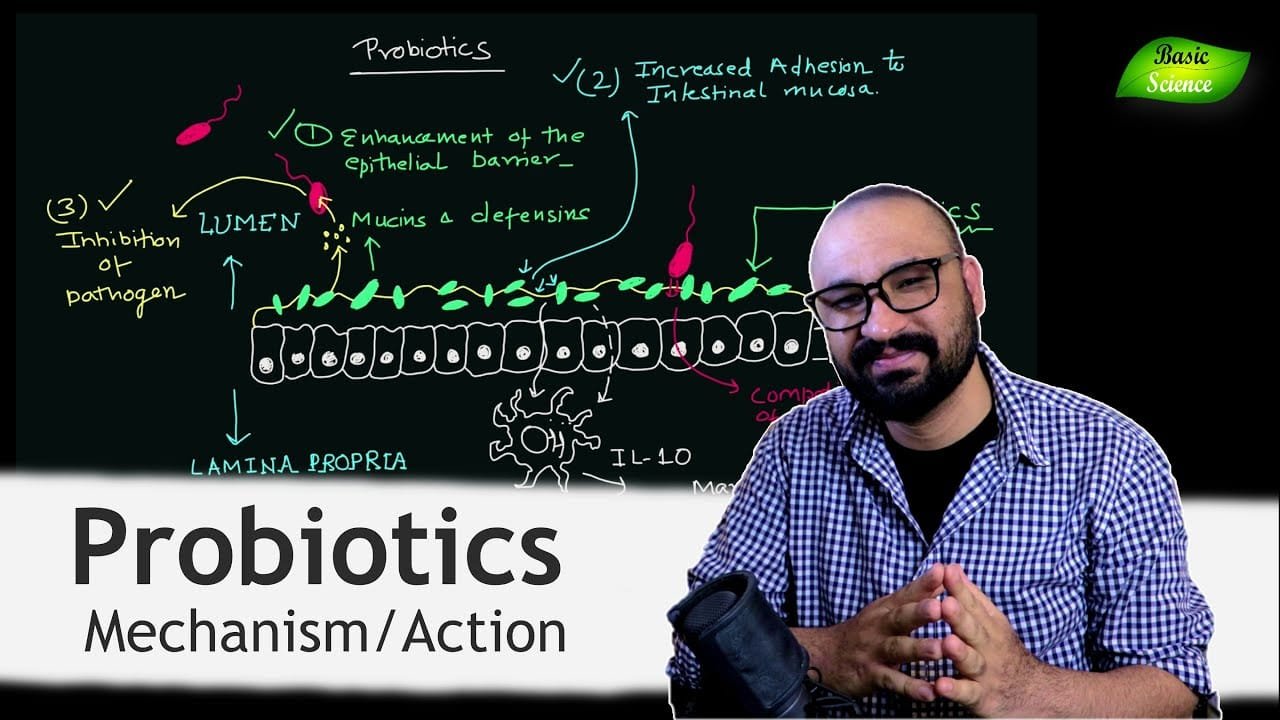
Understanding Probiotics and Their Functions
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host. This section delves into what probiotics are, their relationship with the gut microbiome, and the specific health advantages they may offer.
Defining Probiotics
Probiotics are typically composed of bacteria or yeast. The most common bacterial groups classified as probiotics include Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, each of which contains different species and strains. These microorganisms are similar to beneficial microbes found naturally in the human gut.
Probiotics and the Microbiome
The human microbiome, especially the gut microbiota, plays a crucial role in both health and disease. Probiotics interact with the gut microbiome, providing balance and support to the existing ecosystems of microbes. This includes inhibiting pathogens, modulating the local immune system, and enhancing the gut’s barrier function.
- Interaction with Microbes: Probiotics are known to influence the composition and function of the resident gut microbes.
- Immune Response: They can help stimulate the immune system by enhancing the mucosal immune response.
- Gut Health: By improving barrier integrity, probiotics can prevent the entry of harmful bacteria and promote overall gut health.
Major Health Benefits
Research has substantiated that probiotics can contribute to health in numerous ways:
- Immune System Support: They help in boosting immune defense by enhancing the activity of immune cells.
- Digestive Health: Probiotics are beneficial in managing and preventing gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Recent studies suggest that probiotics may also influence other areas of health, such as skin conditions, allergic reactions, and mental health, by interacting with the gut-brain axis.
- Lactobacillus Strains: Evidence from research suggests these strains can reduce the duration of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and help in treating digestive issues.
- Bifidobacterium Strains: Some studies have observed that these strains can help with irritable bowel syndrome and may enhance the overall gut microbiota composition.
By understanding the actions and benefits of various probiotic strains, one can make informed decisions about incorporating probiotics into their diet for improved health. Discover more about the mechanisms of action of probiotics and how they influence the gut microbiota, or explore the specifics on different probiotic functions.
The Impact of Probiotics on Health Conditions
The human body plays host to an array of microorganisms, with probiotics being some of the beneficial players in the maintenance of health and prevention of various conditions.
Digestive Health and Disorders
Probiotics are often heralded for their beneficial effects on digestive health. They may help manage symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a tricky condition characterized by abdominal pain and altered bowel habits. The implementation of probiotics has been associated with alleviating both diarrhea and constipation. Moreover, individuals with ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease, might find solace in probiotics which have demonstrated promising roles in maintaining remission of this condition.
Immunity and Inflammatory Diseases
The scope of probiotics extends beyond just digestive health. These microscopic helpers may amplify immune function, potentially decreasing the incidence of infections. They also show potential in mitigating symptoms of certain inflammatory diseases, like eczema, where inflammation of the skin produces red, itchy patches. Probiotics might just be the unassuming heroes working silently within the digestive system to fortify the body’s defenses.
Probiotics for Overall Wellbeing
Interesting links between the gut and other aspects of health have come to light; for instance, the potential influence of probiotics on the modulation of obesity and depression. This encapsulates the broader concept that probiotics may help reduce inflammation, a common culprit in countless conditions. The importance of these beneficial bacteria might just transcend the gut, suggesting a ripple effect on the entire wellbeing of the body.
Considerations for Probiotic Use

When it comes to integrating probiotics into one’s diet, it’s essential to consider their type, potential benefits, and safety to ensure they align with individual health needs. The selection process leans heavily on understanding strains and targeted benefits, while safety underscores the importance of discussing probiotic use with healthcare professionals.
Choosing the Right Probiotics
Selecting the most suitable probiotic involves narrowing down specific strains for targeted benefits. Not all probiotics are created equal, and their efficacy fundamentally depends on the type and quality of the strain. Scientific studies underscore Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium as among the most common genera included in probiotic supplements or foods, each with its distinct influence on gut flora. One could venture into the science behind these microorganisms to select probiotics that are appropriate for personal health objectives. It also matters if the product has been tested in clinical trials, as this adds a layer of reassurance regarding its effectiveness.
Safety and Side Effects
The inquiry into the safety of probiotics reveals that while they are generally considered safe, potential side effects can occur, especially in individuals with underlying health issues or those with compromised immune systems. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) doesn’t approve dietary supplements, which includes probiotics, with the same rigor as pharmaceuticals. Therefore, users should understand that the control over safety and side effects isn’t as strict as it would be for prescription medication.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
Checking in with a healthcare provider isn’t just good practice—it’s a pivotal step before starting any new supplement regimen. Doctors can provide valuable insights into how probiotics may interact with existing medications or underlying conditions. They can tap into current scientific insight, including the limitations and cautions involving probiotic use. Healthcare providers act as a gatekeeper to guide their patients through the complexities of probiotic selection, ensuring they step forward effectively and safely.